Perpetual Inventory
Perpetual Inventory
According to the perpetual inventory system, a stock transaction requires an accounting record. If not, it is done at more frequent intervals, like monthly or quarterly. Each warehouse is connected to the appropriate account head.
The Warehouse Account balance will rise when goods are received in a specific warehouse. Similar to when goods are transported from the warehouse, an expense is recorded and the warehouse account's balance is decreased.
1. How to activate perpetual inventory
- Activate Perpetual Inventory:e.
Home > Accounting > Company > Enable Perpetual Inventory
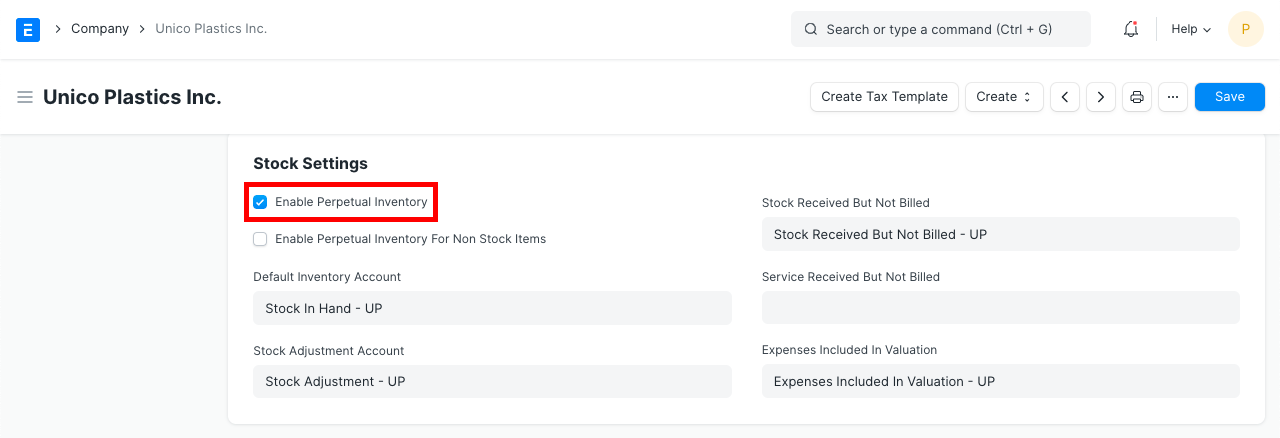
You should be aware that users will need to manually manage the account entries if perpetual inventory is off.
- If not already set up, create the following default accounts for each Company. The new ERPNext accounts automatically establish these accounts.
Account for Default Inventory (Asset)
Receiving stock but not billing it (Liability)
Account for Stock Adjustments (Expense)
Costs Included In The Valuation (Expense)
Price Center
- Create an account head for each account if the user wants to create a separate account for each warehouse. Go to:
Company > Application of Funds (Assets) > Current Asset > Stock Assets > Accounts > Chart of Accounts > Put the same name as the Warehouse account in a new one.
Visit a warehouse right away and connect this account to the facility. This facilitates the filtering and warehouse-based reading of statements.
If the user does not set the account for the warehouse, the system obtains the account head from the parent warehouse for stock transactions and general ledger entries made against the account head specified on the warehouse. If the parent warehouse's account was not configured, the system will utilize the default inventory account from the business master.
EXAMPLE
Take into account the following Chart of Accounts and Warehouse configuration for your business:
Chart of Accounts:
Assets (Dr)
Current Assets
Accounts Receivable Debtors
Stock Assets
Stores
Finished Goods
Work In Progress
Tax Assets
VAT
Liabilities (Cr)
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable
Creditors
Stock Liabilities
Stock Received But Not Billed
Tax Liabilities
Service Tax
Income (Cr)
Direct Income
Sales Account
Expenses (Dr)
Direct Expenses
Stock Expenses
Cost of Goods Sold
Expenses Included In Valuation
Stock Adjustment
Indirect Expenses
Shipping Charges
Customs Duty
2.1 Warehouse - Account Configuration
Stores
Work In Progress
Finished Goods
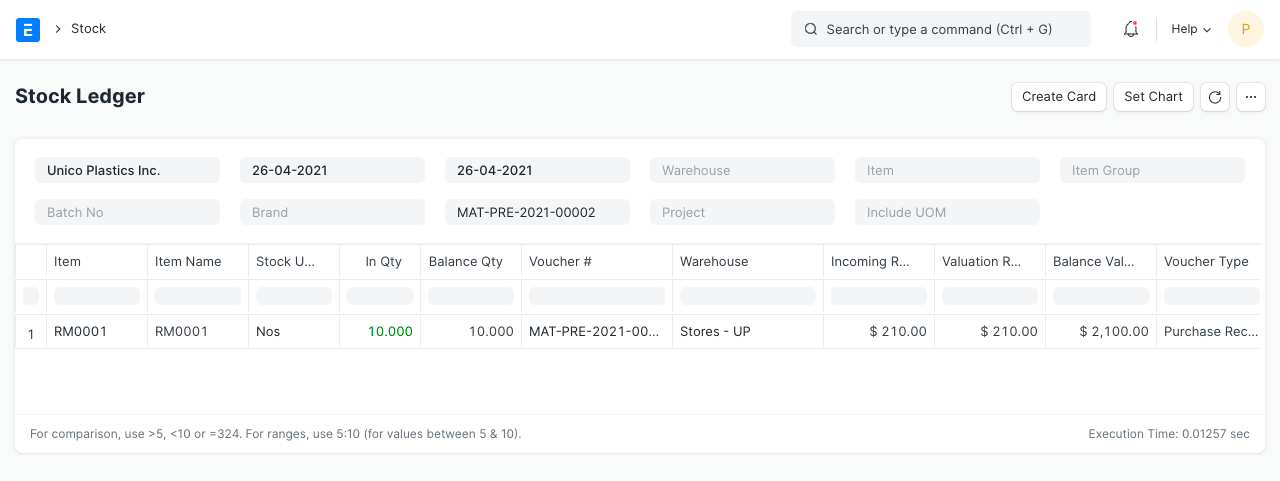
2.2 Purchase Receipt
Let's say you paid $200 for 10 copies of item "RM0001" from vendor "Arcu Vel Quam Fabricators". The purchase receipt's details are as follows:
Supplier: Arcu Vel Quam Fabricators
Items:

Stock Ledger
General Ledger
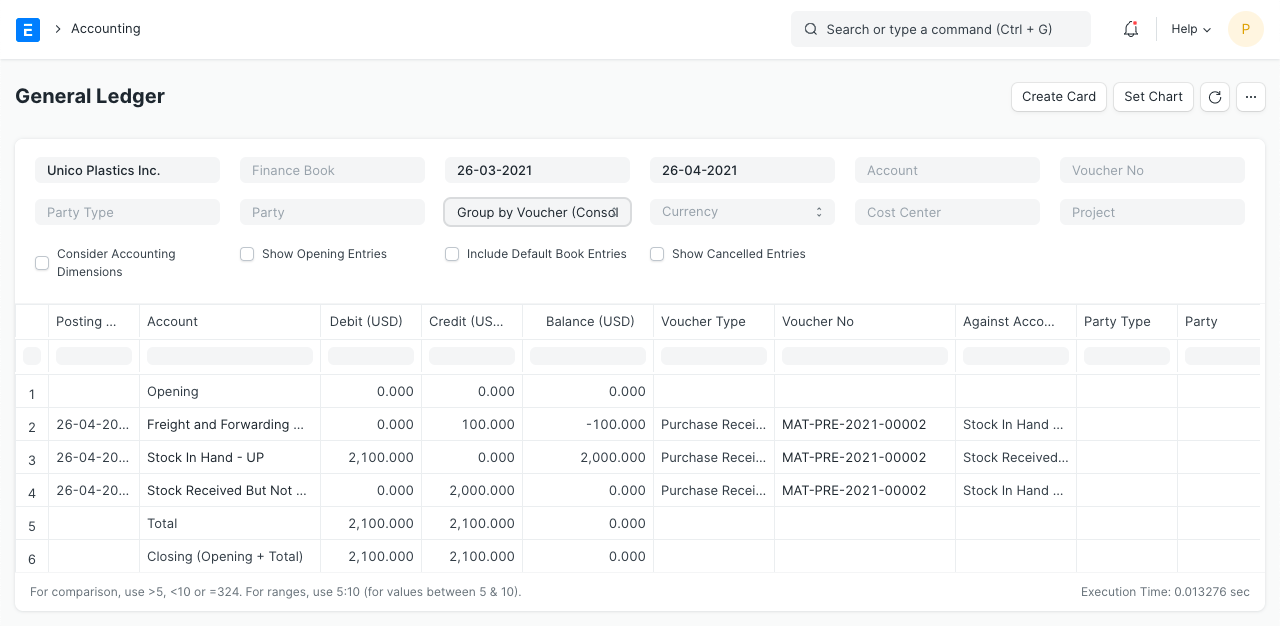
To maintain the double-entry accounting system, "Store" accounts are debited as the stock balance rises through Purchase Receipts, and a temporary account "Stock Receipt But Not Billed" account is credited. In order to avoid double cost booking, the negative expense is recorded concurrently in the account head with the category "Valuation" or "Total and Valuation" in the taxes and charges table for the amount added for valuation purposes.
2.3 Purchase Invoice
You will create a purchase invoice for the aforementioned purchase receipt after you get the supplier's bill. These are the general ledger entries:
General Ledger
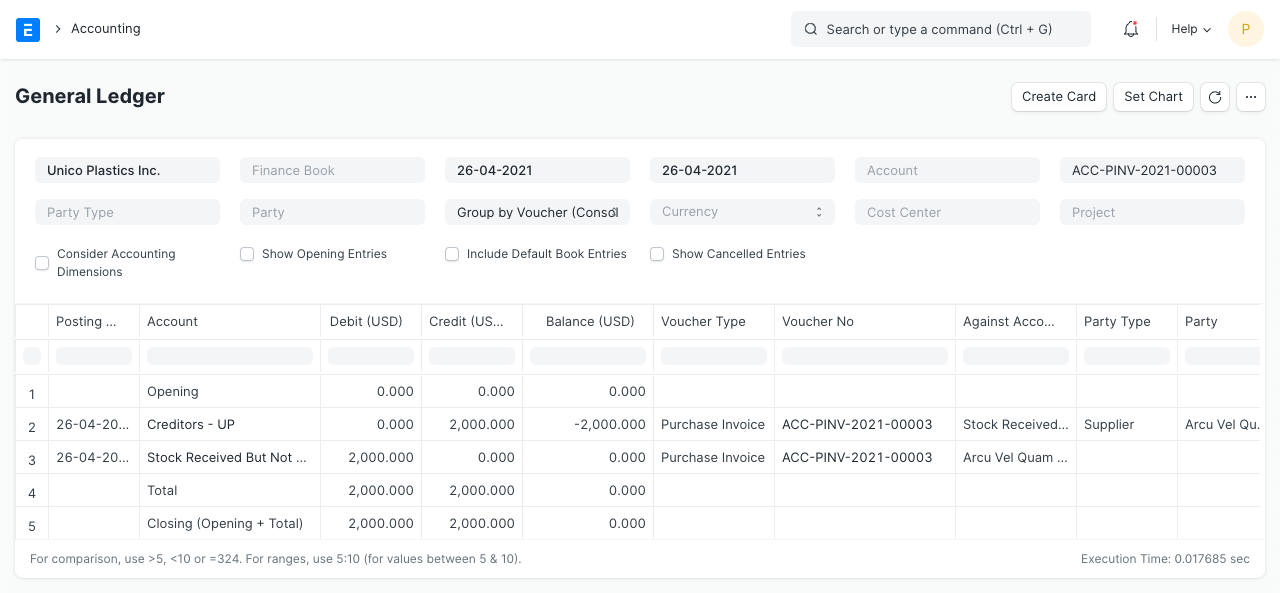
Here, the effect of the Purchase Receipt is cancelled out by a debit to the "Stock Received But Not Billed" account.
2.4 Delivery Note
Say "Utah Automation Services" has asked you to deliver 5 of the item "RM0001" for $300. The delivery note's details are as follows:
Customer: Utah Automation Services
Items:
Stock Ledger
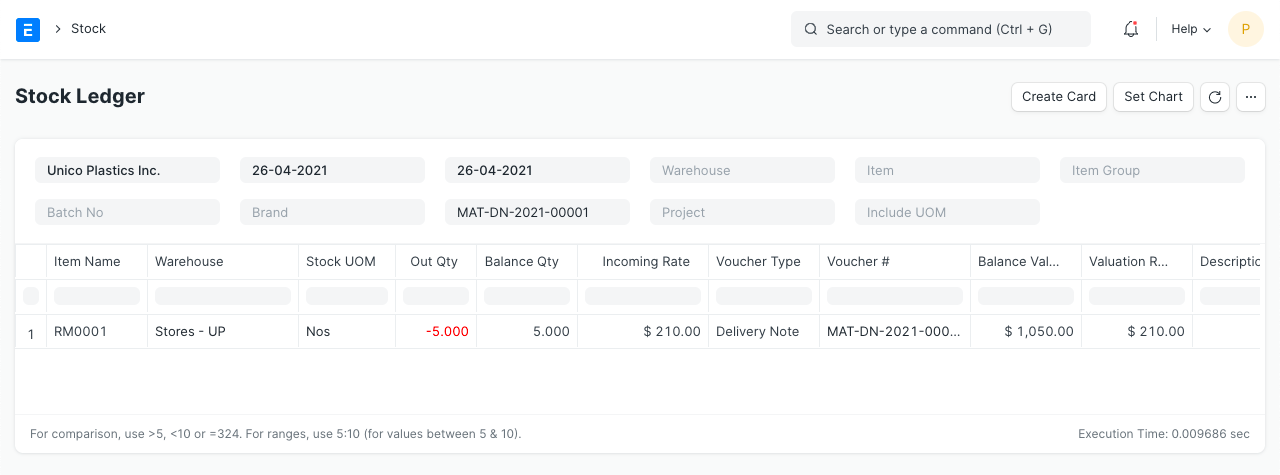
General Ledger
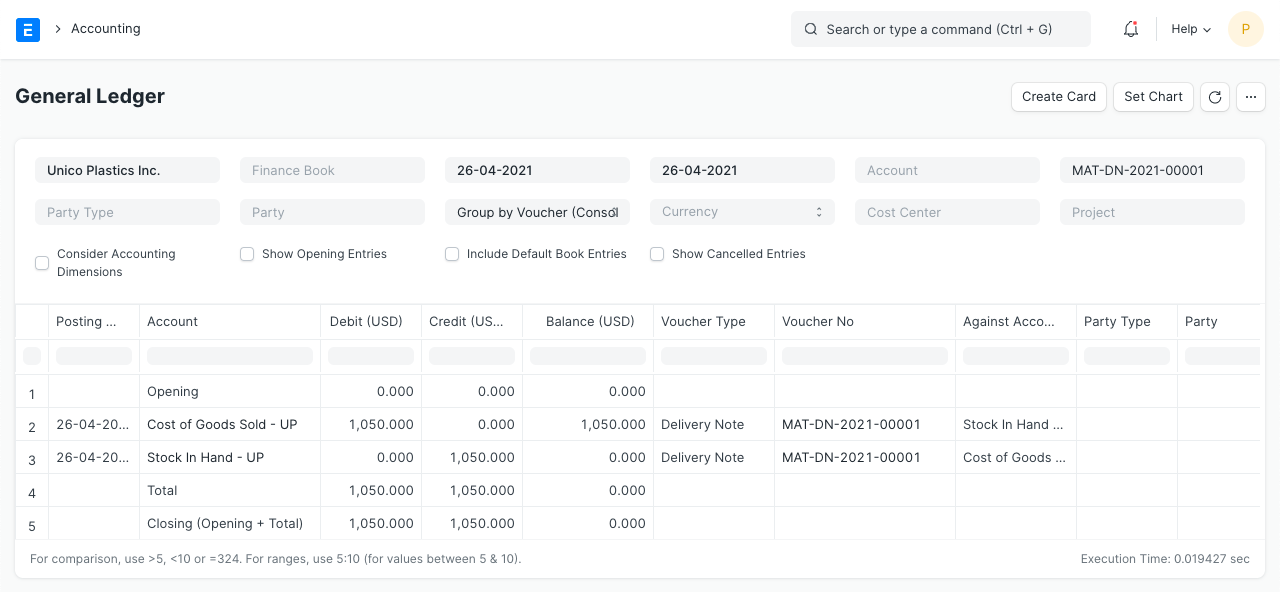
When a product is delivered from the "Stores" warehouse, the "Stores" account is credited and the "Cost of Goods Sold" expenditure account is debited in equal amounts. The overall valuation amount (purchasing cost) of the objects being sold corresponds to the debit/credit amount. Also, the valuation amount is determined using either the actual cost of serialized products or your desired valuation method (FIFO or Moving Average).
2.5 Sales Invoice with Update Stock
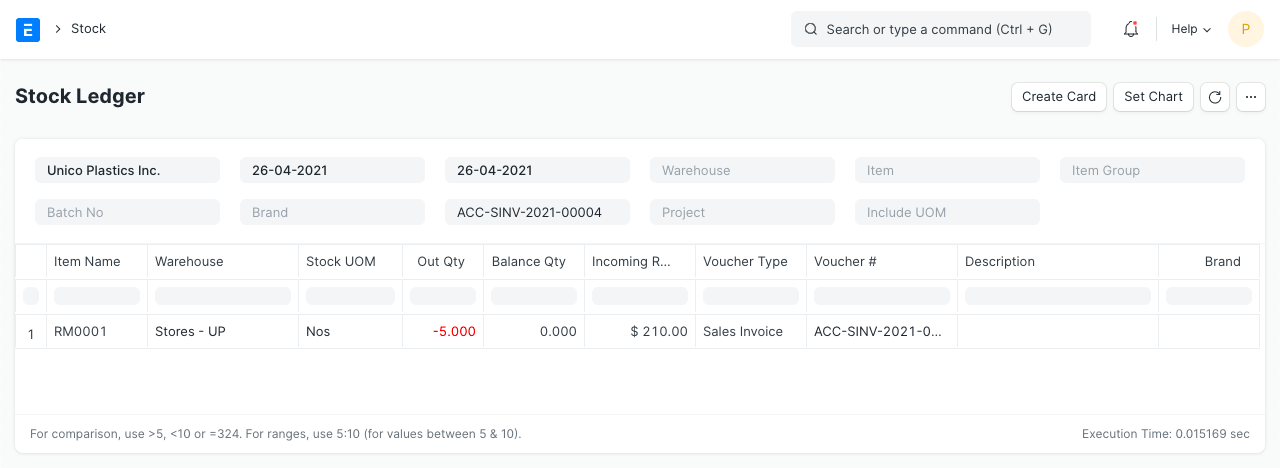
Let's imagine you created a sales invoice immediately with the "Update Stock" options rather than creating a delivery note for the aforementioned order. The sales invoice includes the same information as the delivery note mentioned above.
Stock Ledger
General Ledger
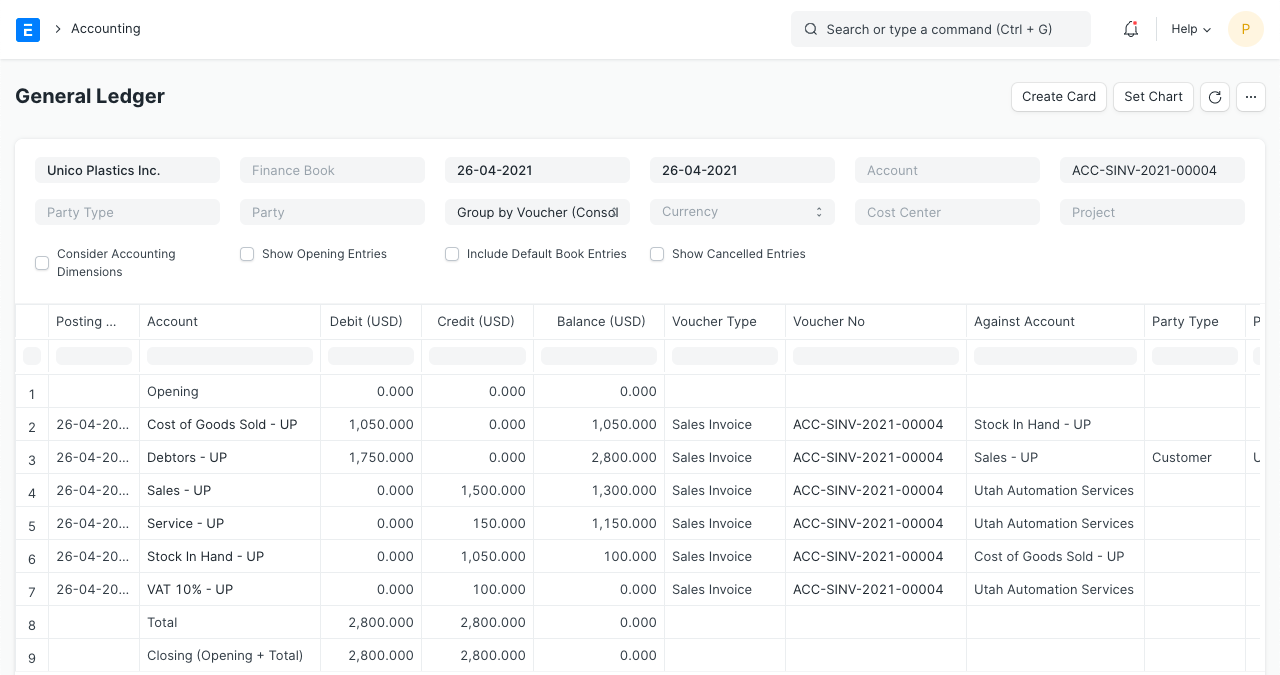
The valuation amount in this case also affects "Stores" and "Cost of Goods Sold" accounts in addition to the usual account entries for an invoice.
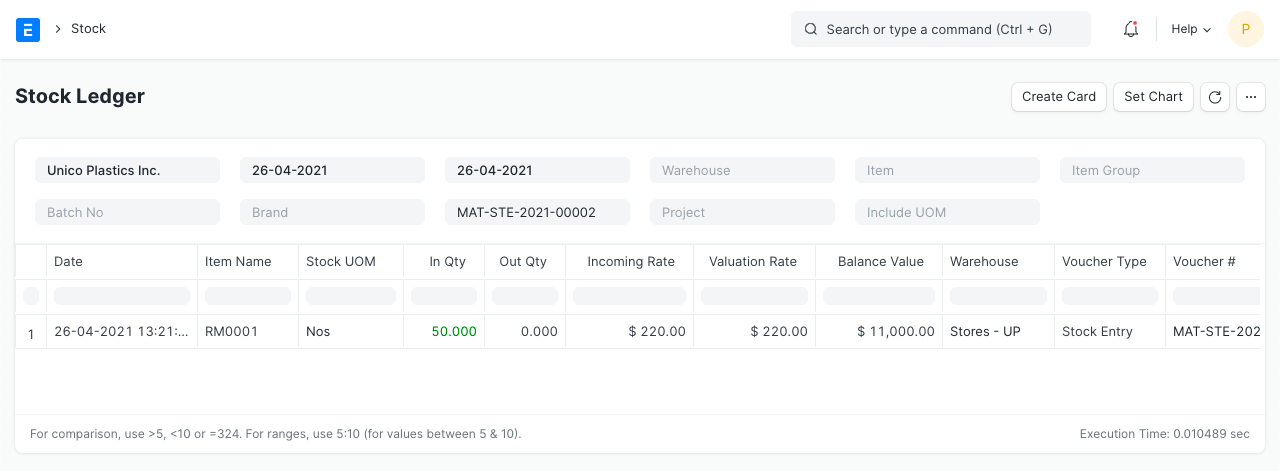
2.6 Stock Entry (Material Receipt)
Items:
Stock Ledger
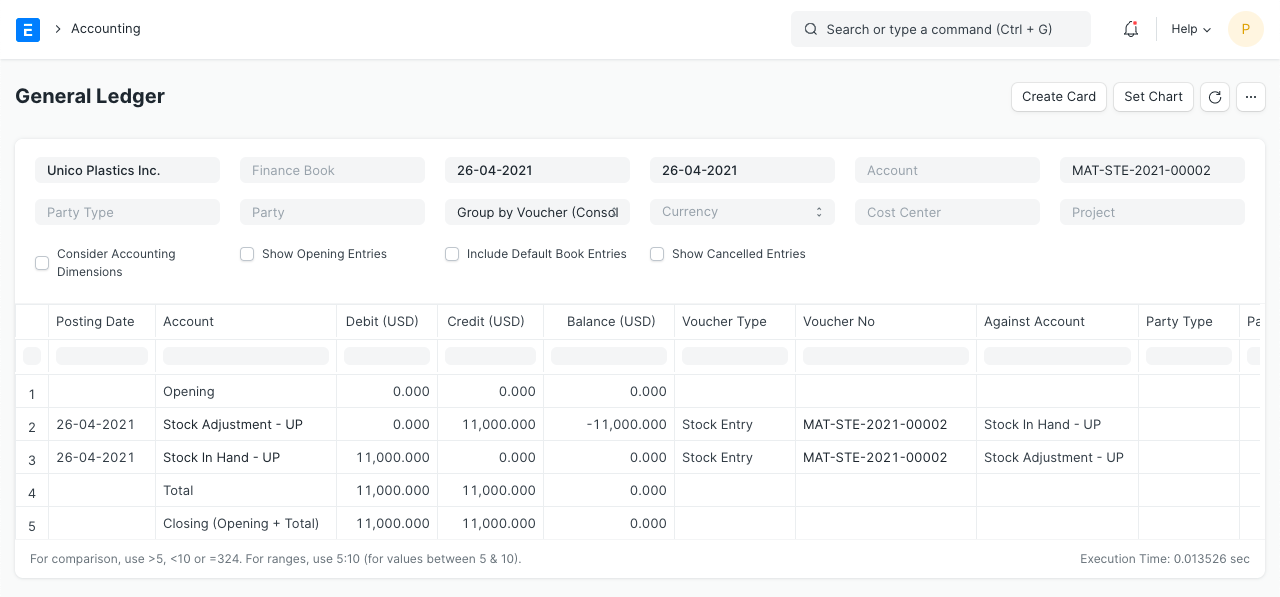
General Ledger
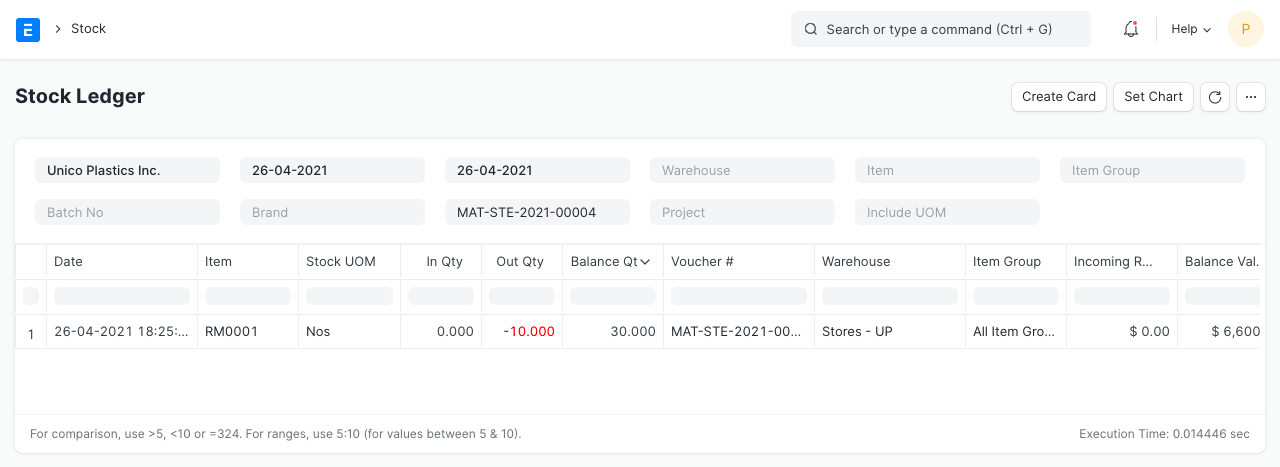
2.7 Stock Entry (Material Issue)
Items:
Stock Ledger
General Ledeger
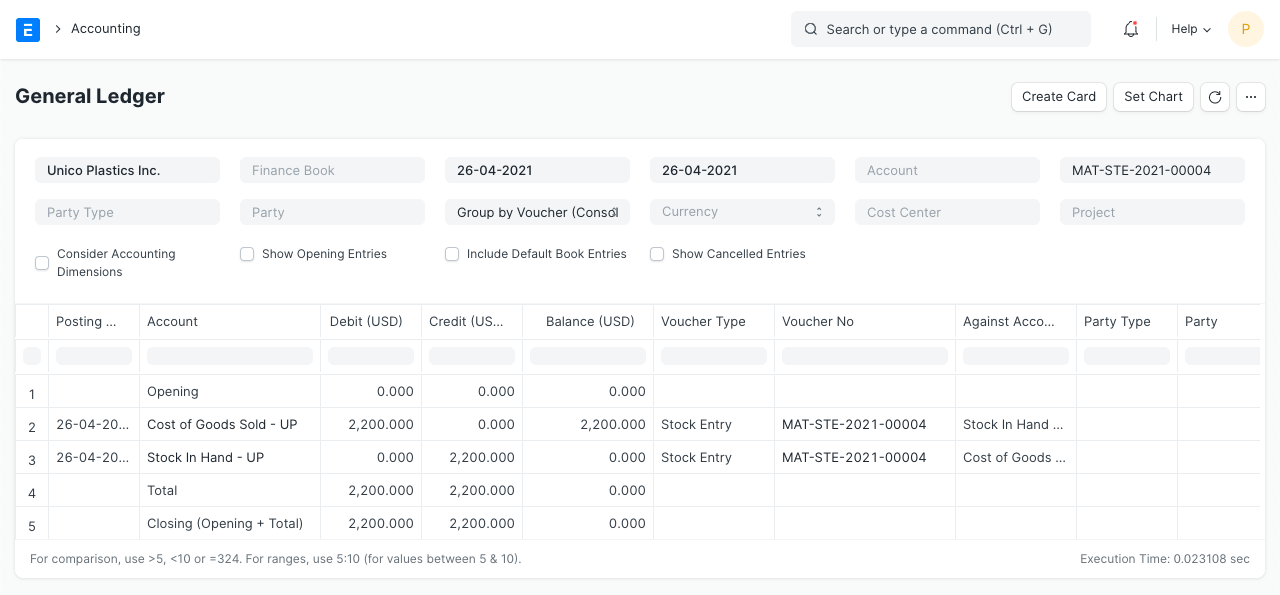
2.8 Stock Entry (Material Transfer)
Items:
Stock Ledger
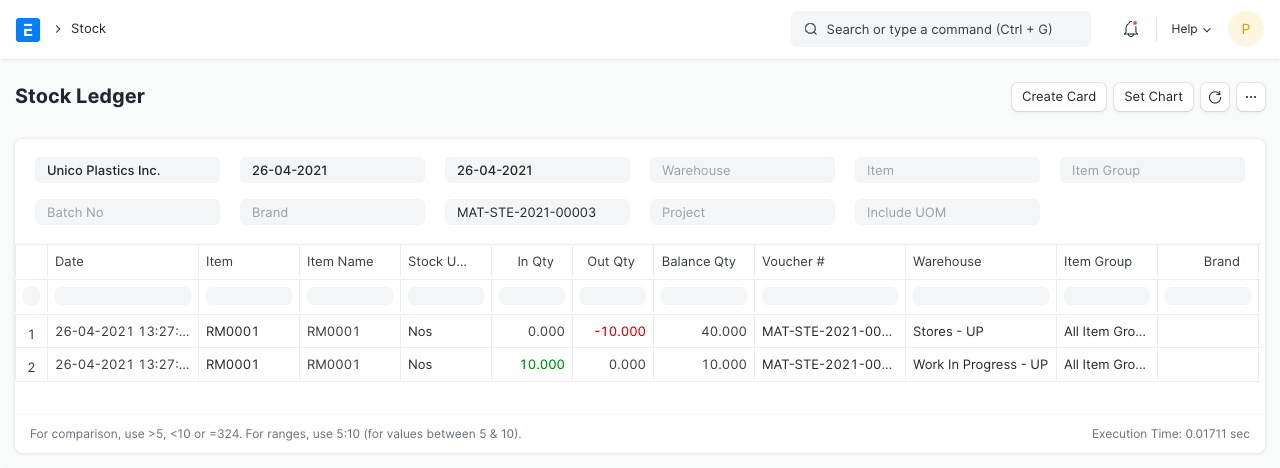
General Ledger