Accounting Entries
Accounts Payable The following example explains the accounting concept: We'll use the company "Tea Stall" as an example to demonstrate how to record accounting transactions for a corporation.
Mama (the proprietor of the tea shop) invests Rs. 25000 to launch the enterprise.
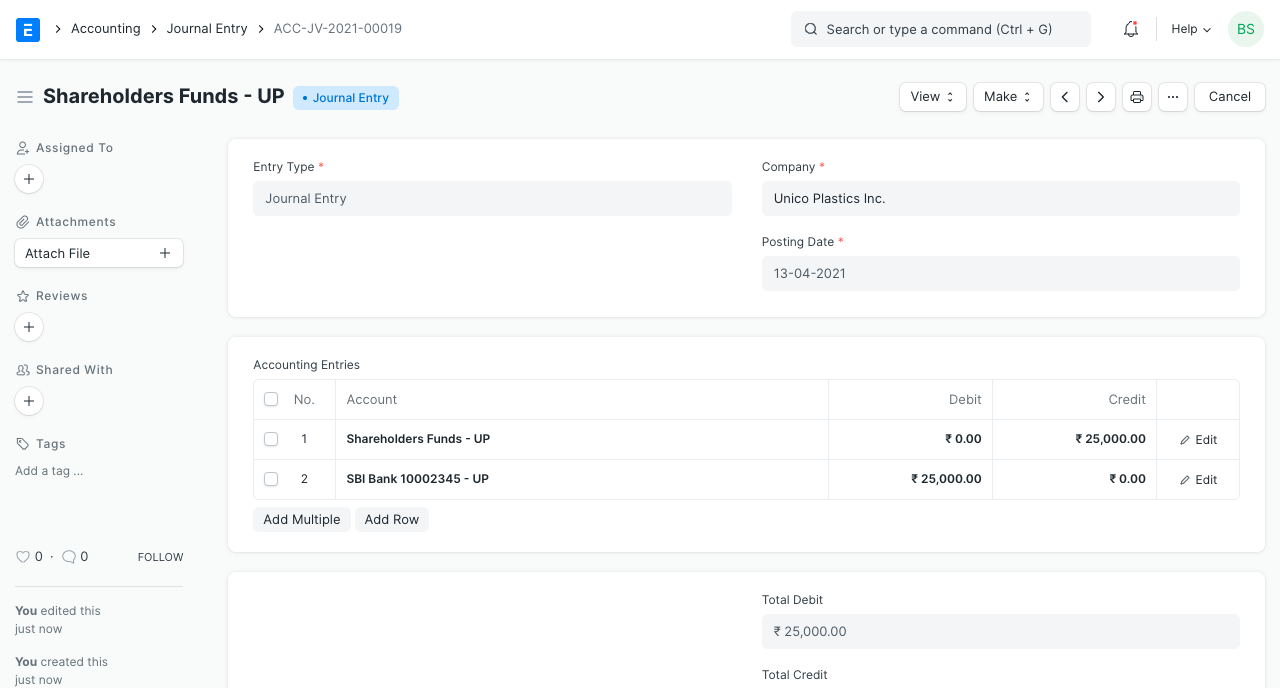
1. Investment
Mama put $25,000 into the company in the hopes of making a profit. In other words, firm will eventually be required to pay Rs. 25000 to Mama. Account "Mama" is credited because it is a liability account. The investment will result in an increase in the company's cash balance. Cash will be debited because it is an asset to the organization.
The business urgently need raw goods (tea, sugar, milk, etc.) as well as equipment (stove, teapot, cups, etc.). In order to earn some credit, he chooses to purchase them from the neighborhood general shop, "Super Bazaar," whose proprietor is a friend. He spent Rs. 2800 on equipment and Rs. 2200 on raw ingredients. Out of the total cost of Rs. 5000, he pays Rs. 2000. Geer ERP allows for the recording of this utilizing a Payment Entry.
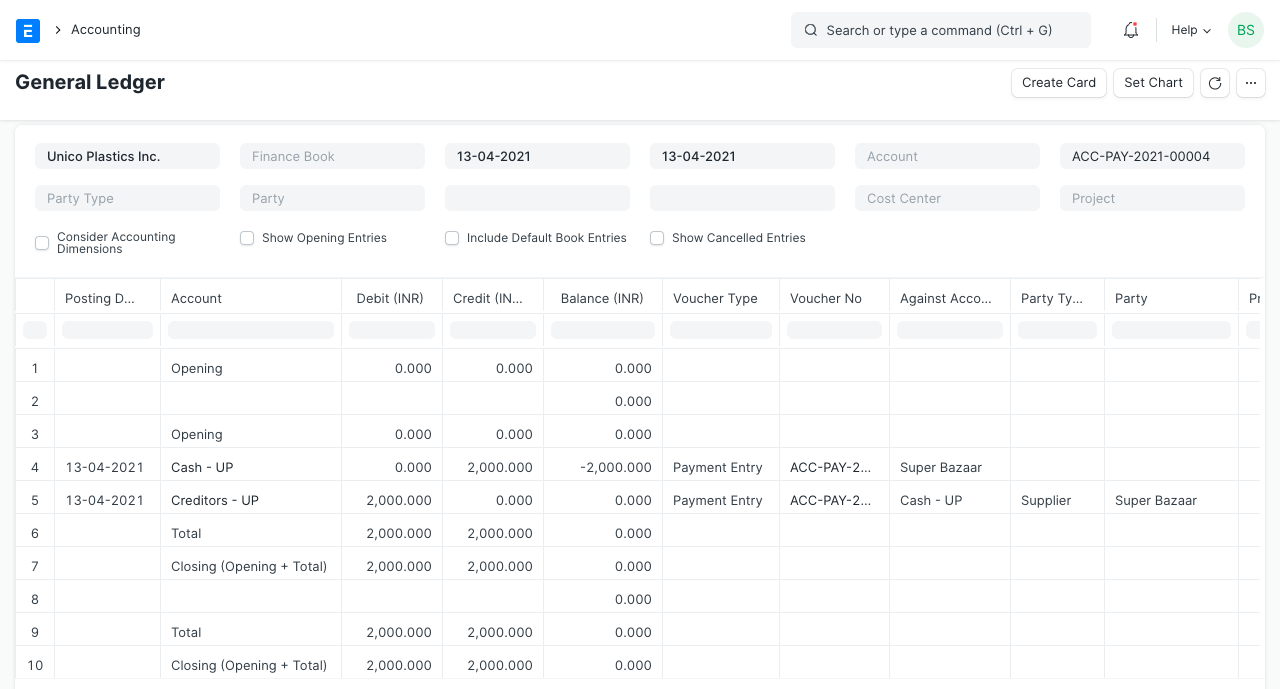
2. Assets
Raw materials are the company's "Current Assets" since they are used in day-to-day operations, whereas equipment is a "Fixed Asset" because of its lengthy lifespan. In order to raise the value, "Equipments" and "Stock in Hand" accounts have been debited. He pays $2,000, therefore the "Cash" account will be decreased by that sum and credited. He also owes $3,000 to "Super Bazaar," thus Super Bazaar will also receive a $3,000 credit.
In order to analyze daily sales, Mama (who handles all entries) chooses to book sales at the end of each day. 325 cups of tea are sold at the tea booth by the conclusion of the first day, resulting in net sales of Rs. 1625. Owner cheerfully records first-day sales.
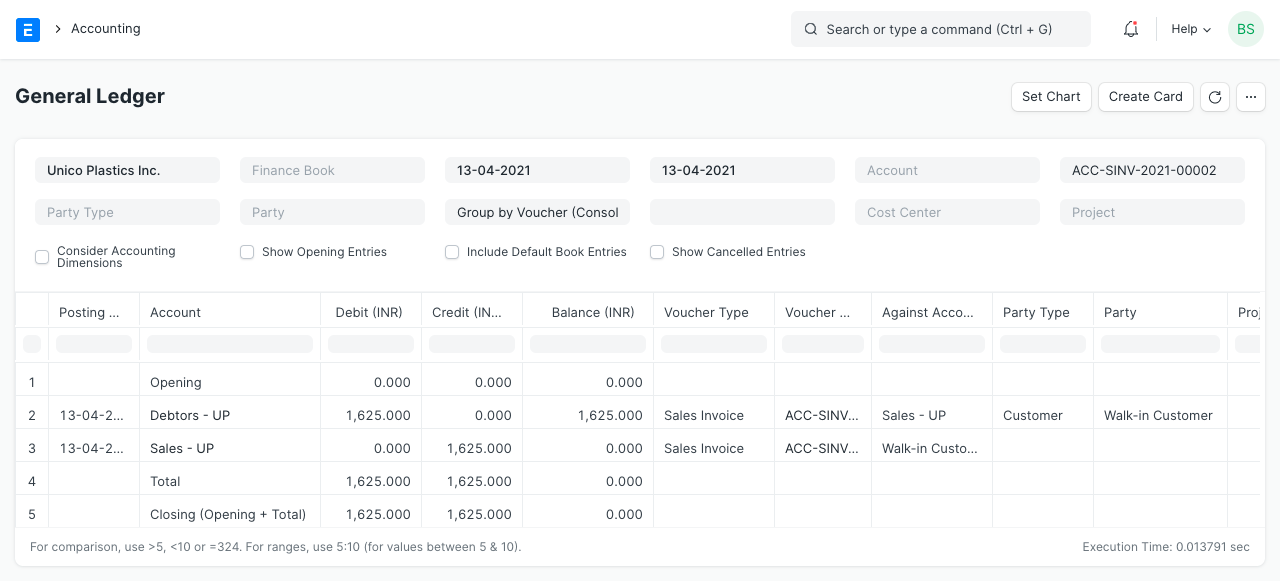
3. Income
The "Sales of Tea" account has received income, which has been credited to enhance its value. The same amount will then be deducted from the "Cash" account. For example, if it costs Rs. 800 to brew 325 cups of tea, "Stock in Hand" will be lowered by that amount (Cr), and the same expense will also be recorded in the "Cost of Goods Sold" account.
At the end of the month, the business paid the stall's rent of Rs. 5000 and the pay of one new hire, who received Rs. 8000 in salary.
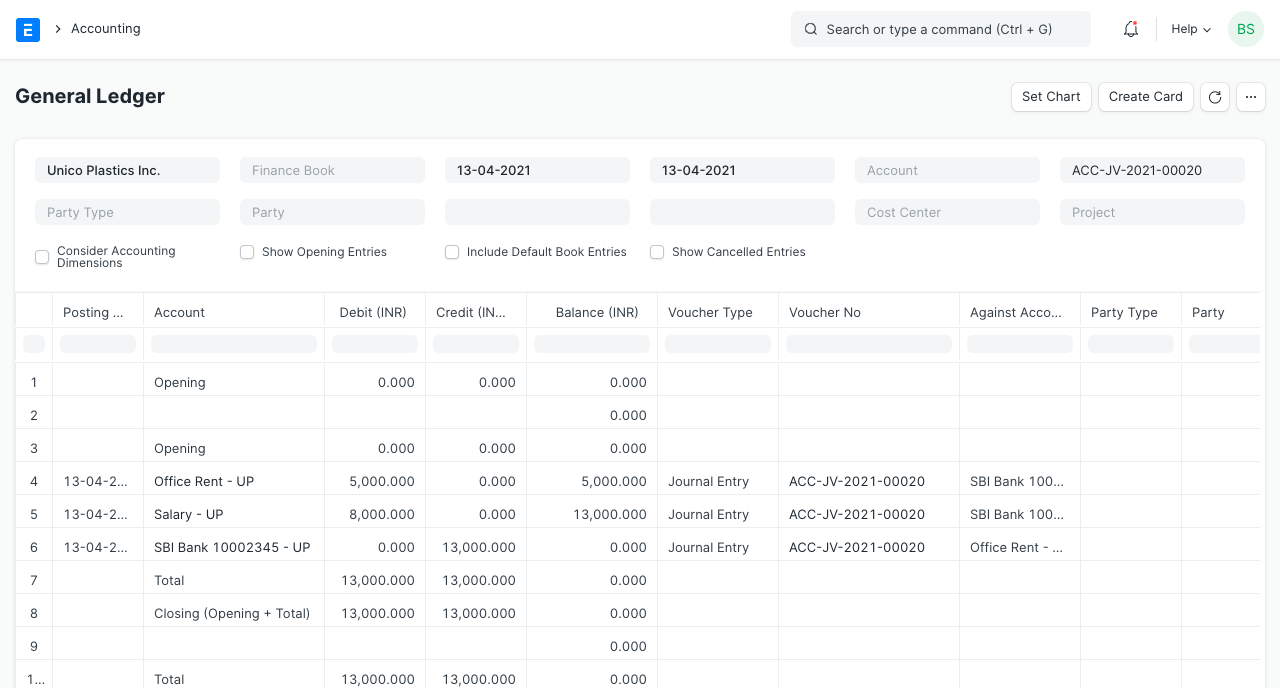
4. Booking Profit
As the month went on, the corporation bought more raw materials for the industry. He records profits to bring the "Balance Sheet" and "Profit and Loss Statements" statements into balance after a month. Profit is a liability for the corporation because it belongs to Mama and not the company (it has to pay it to Mama). The profit has not yet been booked when the Balance Sheet is unbalanced, that is, when Debit exceeds Credit. The profit and loss accounts must be updated in order to book a profit. The profit/loss statement is reset after the profit/loss is moved to the liability account. A Period Closing Voucher is used for this.
Reason: The company's net revenues and expenses are each of Rs. 40,000 and Rs. 20,000. As a result, the company earned Rs. 20,000. The "Profit or Loss" account has been debited and the "Capital Account" has been credited to create the profit booking entry. The company has a net cash balance of Rs. 44,000 and some raw goods worth Rs. 1000 are on hand.